
Understanding Your Fire Extinguishers: A Guide to Class A, B, C, and D Fires

Fire extinguishers are essential tools for combating small fires in their early stages. However, not all fires are the same, and using the wrong type of extinguishers can be ineffective or even dangerous. This guide will help you understand the different types of fire extinguishers and how to use them properly.
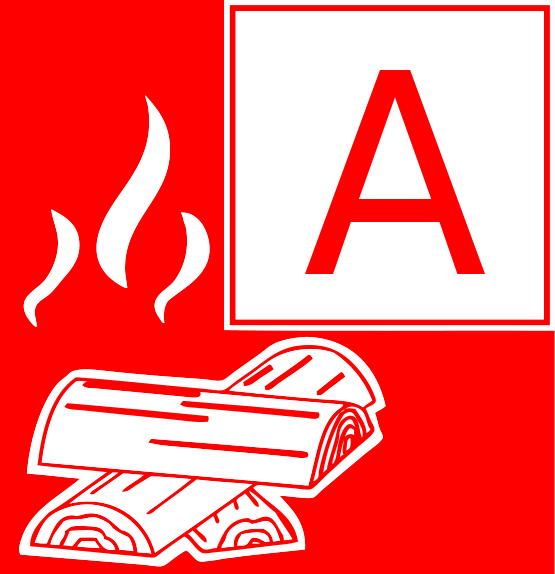
Class A Fires: Combating Ordinary Combustibles
Class A fires involve ordinary combustible materials such as wood, paper, cloth, rubber, and some types of plastics. These materials are common in most homes and workplaces, making Class A fires one of the most frequent types of fire emergencies.
Characteristics of Class A Fire Extinguishers:
Class A fire extinguishers are designed to combat fires involving these ordinary combustibles. They work by cooling the fire with water or by using foam or dry chemical agents to remove the heat, which is a crucial element of the fire triangle (heat, fuel, oxygen).
Limitation of Class A Fire Extinguishers:
While effective for Class A fires, these extinguishers are not suitable for fires involving flammable liquids, electrical equipment, or combustible metals. Using a Class A extinguisher on such fires can be dangerous and may worsen the situation.

Class B Fires: Tackling Flammable Liquids
Class B fires involve flammable liquids and gases, such as gasoline, oil, grease, paint, and solvents. These fires are common in environments where such substances are stored or used, including garages, workshops, and industrial settings.
Types of Extinguishers for Class B Fires:
Class B fire extinguishers typically use foam, carbon dioxide (CO2), or dry chemical agents. These extinguishers work by smothering the fire, cutting off the oxygen supply, and preventing the fire from spreading.
The Importance of Smothering Agents:
Using a smothering agent is crucial in Class B fires because simply cooling the fire (as in Class A) is not effective. The agent must create a barrier between the fuel and the oxygen in the air to successfully extinguish the flames.

Class C Fires: Safely Extinguishing Electrical Fires
Class C fires involve electrical equipment such as wiring, circuit breakers, machinery, appliances, and electronic devices. These fires are particularly hazardous because they can pose a risk of electrocution.
Specific Extinguishers for Class C Fires:
Class C fire extinguishers are typically filled with non-conductive extinguishing agents like dry chemicals or CO2. These extinguishers are designed to safely extinguish electrical fires without the risk of conducting electricity back to the user.
Safety Precautions When Dealing With Electrical Fires:
When dealing with a Class C fire, it’s critical to first disconnect the electrical source, if possible, before attempting to extinguish the fire. Using water-based extinguishers on electrical fires can cause electrical shock and is extremely dangerous.

Class D Fires: Handling Combustible Metals
Class D fires involve combustible metals such as magnesium, titanium, potassium, and sodium. These metals burn at extremely high temperatures and react violently with water, making these fires highly dangerous.
Specialised Equipment for Class D Fires:
Class D fire extinguishers contain specialised dry powder agents that work by separating the fuel from the oxygen in the air or by removing the heat. These extinguishers are designed specifically for metal fires and are not suitable for use on other types of fires.
The Hazards of Class D Fires:
Due to the highly reactive nature of combustible metals, Class D fires are particularly hazardous and should only be handled by professionals trained in dealing with such incidents. Using the wrong extinguishing method can cause explosions or intensify the fire.

Multi-Purpose Fire Extinguishers: Versatile but Limited
Limitations of Multi-Purpose Extinguishers
While multi-purpose extinguishers are effective for many types of fires, they may not be suitable for all situations. For example, they are not appropriate for Class D (metal) fires or for large industrial fires that may require specialised equipment. It’s important to assess the specific fire risks in your environment before relying solely on a multi-purpose extinguisher.
Advantages of Multi-Purpose Extinguishers
Multi-purpose fire extinguishers, commonly labelled as ABC extinguishers, are designed to handle Class A, B, and C fires. They are versatile and convenient, making them a popular choice for homes and businesses.
Using a Fire Extinguisher: The PASS Method
Step-by-step instructions on using a fire extinguisher.
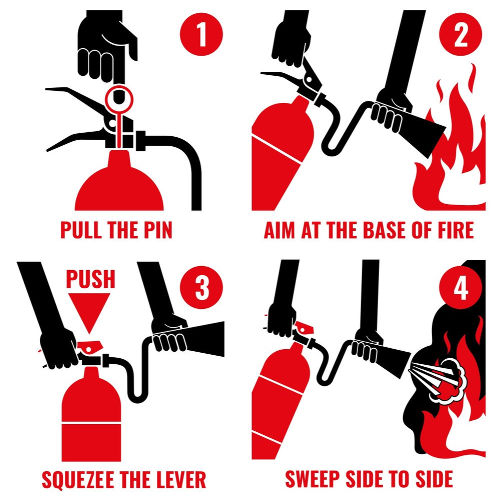
Importance of Knowing Extinguisher Locations:
Ensure that fire extinguishers are easily accessible and that everyone in the household or workplace knows their locations. Practicing the PASS method in a controlled environment can build confidence and improve response times during an actual emergency.
Catch our newest videos on LinkedIn!
Conclusion: Prioritise Safety with the Right Fire Extinguishers
Having the appropriate fire extinguishers for your specific needs is a critical aspect of fire safety. Investing in professional training on fire extinguisher use and regularly practicing with your team can save lives. At Signature Fire Protection, we’re committed to helping you stay safe and compliant with the best fire protection solutions. Contact us today to ensure you have the right fire extinguishers for every potential emergency.
Latest post
Escape the Fire: Building a Life-Saving Fire Escape Plan
How Fire Safety Training Protects Your Business
Understanding Your Fire Extinguishers: A Guide to Class A, B, C, and D Fires
© 2024 All Rights Reserved. Powered by Digital Media Center Designed by John Cole Creative

